「Spring Boot」を使うと、Javaベースのアプリケーションフレームワーク「Spring Framework」に準ずるWebアプリケーションを手軽に構築することが可能です。
今回の記事では、Spring Bootを使用してWeb APIを作成し、さらにJavaScript帳票ライブラリ「ActiveReportsJS(アクティブレポートJS)」を使用してブラウザから帳票出力を行う方法をご紹介します。
MySQLにテーブルの追加
MySQLに今回使用するデータを格納するテーブルを作成します。MySQLのセットアップ方法は以下の記事で解説しています。
コマンドプロンプトやターミナルなどから以下のコマンドを実行し、MySQLを起動します。
mysql -u root -pパスワードを入力し、MySQLが起動出来たら、以下のコマンドを入力し、データベース「test」を作成します。
CREATE DATABASE test;次にUSE文を使い、「test」を使用するデータベースとして設定します。
USE test今回の帳票で表示する請求書情報を格納するテーブル「invoice」を作成します。
CREATE TABLE invoice (id INT, billno VARCHAR(256), slipno VARCHAR(256), customerid INT, customername VARCHAR(256), products VARCHAR(256), number INT, unitprice INT, date DATETIME);テーブルを作成したら、INSERT文を使ってデータを追加していきます。
INSERT INTO invoice VALUES (1,'WS-DF502','GB465',1, '長崎カントリーフーズ', 'コーヒー 250 ml', 100, 100, '2020-01-05 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO invoice VALUES (2,'WS-DF502','GB465',1, '長崎カントリーフーズ', '紅茶 350 ml', 300, 120, '2020-01-05 00:00:00');
INSERT INTO invoice VALUES (3,'WS-DF502','DK055',1, '長崎カントリーフーズ', '炭酸飲料 (オレンジ) 350 ml', 200, 120, '2020-01-09 00:00:00');データを追加したら、SELECT文で確認します。
SELECT * from invoice正しくデータが登録/取得されていれば、次のように結果が表示されます。

Web APIの作成
データの登録が完了したら、次はSpring BootでMySQLからデータの参照を行うWeb APIを作成します。IDEとして、Eclipseベースの開発ツール「Spring Tool Suite」を使用します。また、こちらからダウンロードできる「Pleiades プラグイン」を使用して日本語化を行っています。
- [ファイル]⇒[新規]⇒[Spring スターター・プロジェクト]を選択します
- [新規 Spring スターター・プロジェクト]ダイアログで、[名前]に”reporting-demo”と入力して、[次へ]ボタンをクリックします。
- [新規 Spring スターター・プロジェクト依存関係]ダイアログで、以下の4つをチェックして、[完了]ボタンをクリックすると、プロジェクトが作成されます。
- Web→Spring Web
- SQL→MySQL Driver
- SQL→Spring Data JPA
- テンプレート・エンジン→Thymeleaf
次に「src/main/resources/application.properties」ファイルに以下を追加し、MySQLとの接続設定を行います。また、日付データを扱うのでタイムゾーンの設定も行います。
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=*********
spring.jackson.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss
spring.jackson.time-zone=Asia/Tokyo「spring.datasource.url」の項目に設定してるURL中の「test」は冒頭で作成したMySQLのデータベース名です。
次にエンティティクラスを作成します。「src/main/java」配下で、[ファイル]⇒[新規]⇒[クラス]を選択し、[名前]に「Invoice」と入力し、[完了]をクリックし、「Invoice.java」が作成されたら以下のように記述します。
package com.example.demo;
import java.sql.Timestamp;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "invoice")
public class Invoice {
@Id
@Column(name = "id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name = "billno")
private String billno;
@Column(name = "slipno")
private String slipno;
@Column(name = "customerid")
private Integer customerid;
@Column(name = "customername")
private String customername;
@Column(name = "products")
private String products;
@Column(name = "number")
private Integer number;
@Column(name = "unitprice")
private Integer unitprice;
@Column(name = "date")
private Timestamp date;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBillNo() {
return billno;
}
public void setBillNo(String billno) {
this.billno = billno;
}
public String getSlipNo() {
return slipno;
}
public void setSlipNo(String slipno) {
this.slipno = slipno;
}
public Integer getCustomerId() {
return customerid;
}
public void setCustomerId(Integer customerid) {
this.customerid = customerid;
}
public String getCustomerName() {
return customername;
}
public void setCustomerName(String customername) {
this.customername = customername;
}
public String getProducts() {
return products;
}
public void setProducts(String products) {
this.products = products;
}
public Integer getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(Integer number) {
this.number = number;
}
public Integer getUnitPrice() {
return unitprice;
}
public void setUnitPrice(Integer unitprice) {
this.unitprice = unitprice;
}
public Timestamp getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Timestamp date) {
this.date = date;
}
}次に「リポジトリ」という機能を使って、データベースに対するCRUD処理を実装します。今回は”JpaRepository”という既存のクラスを継承して使用します。「src/main/java」配下で、[ファイル]⇒[新規]⇒[クラス]を選択し、[名前]に「InvoiceRepository」と入力し、[完了]をクリックし、「InvoiceRepository.java」が作成されたら以下のように記述します。
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface InvoiceRepository extends JpaRepository<Invoice, Integer> {
}次は、フロントエンドからのリクエストとデータベース操作処理をつなぐ、「サービス」処理を作成します。「src/main/java」配下で、[ファイル]⇒[新規]⇒[クラス]を選択し、[名前]に「InvoiceService」と入力し、[完了]をクリックし、「InvoiceRepository.java」が作成されたら以下のように記述します。
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
@Service
@Transactional
public class InvoiceService {
@Autowired
InvoiceRepository invoiceRepository;
public List<Invoice> findAll() {
return invoiceRepository.findAll();
}
public Invoice save(Invoice order) {
return invoiceRepository.save(order);
}
public void deleteById(Integer id) {
invoiceRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}バックエンド処理の仕上げに、コントローラを作成します。「src/main/java」配下で、[ファイル]⇒[新規]⇒[クラス]を選択し、[名前]に「InvoiceService」と入力し、[完了]をクリックし、「InvoiceRepository.java」が作成されたら以下のように記述します。
package com.example.demo;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@CrossOrigin
@RequestMapping("api/invoice")
public class InvoiceController {
@Autowired
private InvoiceService invoiceService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
List<Invoice> getInvoice() {
return invoiceService.findAll();
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
Invoice insertInvoice(@Validated @RequestBody Invoice invoice) {
return invoiceService.save(invoice);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
Invoice updateInvoice(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @Validated @RequestBody Invoice invoice) {
invoice.setId(id);
return invoiceService.save(invoice);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)
void deleteInvoice(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
invoiceService.deleteById(id);
}
}
Web APIの実行
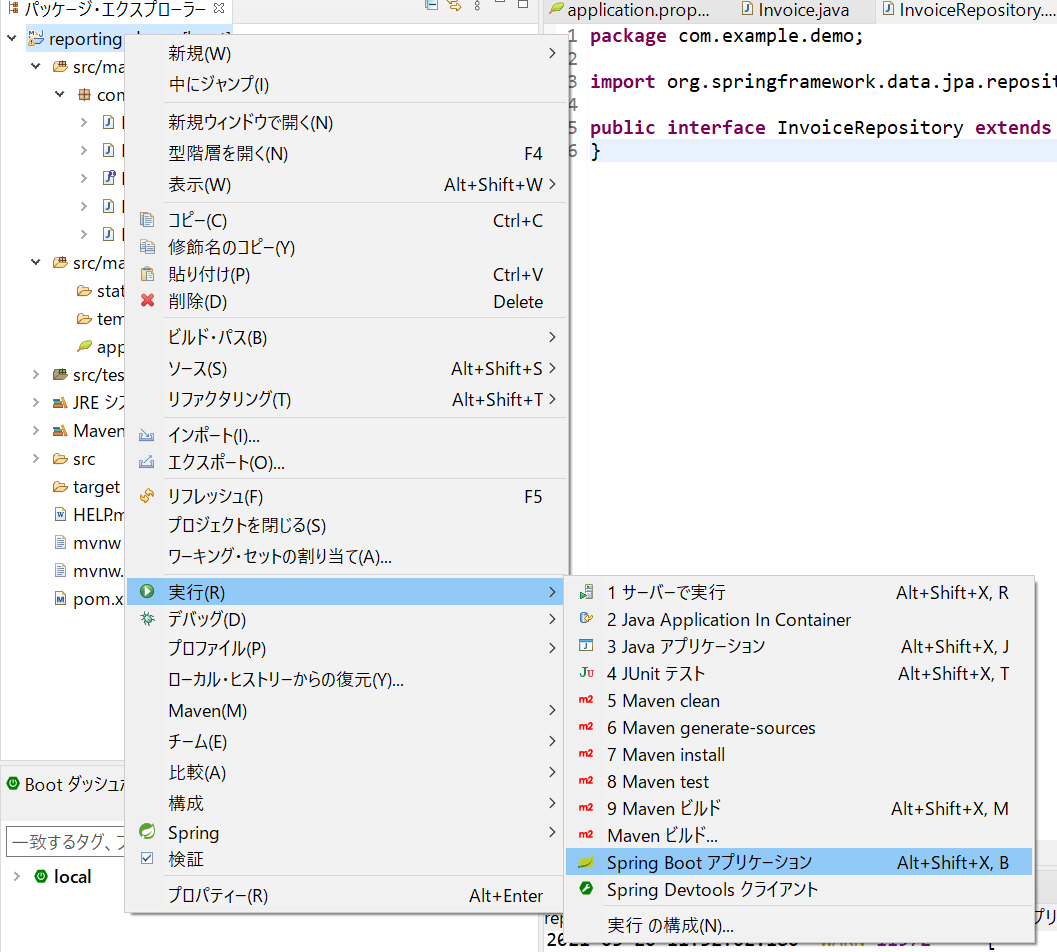
以上でWeb APIの実装は完了です。[パッケージエクスプローラー]で右クリックし、[実行]⇒[Spring Boot アプリケーション]を選択し、APIを起動します。
APIを起動したら、Postmanなどのツールを使用してリクエストを送信し、テストしてみます。
GET(参照)
「http://localhost:8080/api/invoice」に対してGETリクエストを実行します。MySQLに登録した3件のデータが取得されます。
POST(登録)
「http://localhost:8080/api/invoice」に対してPOSTリクエストを実行します。以下のJSONをBodyに追加して実行します。
{
"id": 4,
"products": "ピリピリ ビール",
"number": 80,
"date": "2021-01-12T00:00:00",
"billNo": "WS-DF502",
"customerName": "長崎カントリーフーズ",
"slipNo": "YJ215",
"customerId": 1,
"unitPrice": 100
}PUT(更新)
「http://localhost:8080/api/invoice/4」に対してPUTリクエストを実行します。以下のJSONをBodyに追加し、先ほど登録したデータの製品名(products)の部分を更新します。
{
"id": 4,
"products": "バードワイン",
"number": 80,
"date": "2021-01-12T00:00:00",
"billNo": "WS-DF502",
"customerName": "長崎カントリーフーズ",
"slipNo": "YJ215",
"customerId": 1,
"unitPrice": 100
}DELETE(削除)
「http://localhost:8080/api/invoice/4」に対してDELETEリクエストを実行し、先ほど登録したデータを削除します。
さいごに
以上がSpring Bootで簡単なWeb APIを実装する方法でした。後半の記事では、このAPIとActiveReportsJSを連携させて帳票出力処理をSpring Bootに実装していきたいと思います。
製品Webサイトでは製品の機能を手軽に体験できるデモアプリケーションやトライアル版も公開しておりますので、こちらもご確認ください。
また、ご導入前の製品に関するご相談、ご導入後の各種サービスに関するご質問など、お気軽にお問合せください。
